Getting Support
Please use the appropriate channel to request support – Enterprise customers should file a support ticket or work directly with their Customer Success Manager. For everyone else, please use Stardog Community.
Cloud users (Free & Essentials) should use the dedicated forum in Stardog Community. Cloud Premium and Enterprise customers should contact their CSM or use the normal support portal.
To see a comparison of our support offerings, visit stardog.com/support.
Reporting an Issue
When reporting an issue, please include the following information in your report:
- A complete description of the problem you are having. This includes describing the expected behavior, as well as the observed behavior in as much detail as possible.
- A diagnostics report produced by the
stardog-admin diagnostics reportfor single node deploys. See Creating a Diagnostics Report for additional information. - Other information as you are able:
- Approximately when you hit this issue (so we can reference in the logs)
- Your Stardog version
- Your operating system and any other system info
- Which JVM you are using
- If you are reporting a query performance issue, please see Query Performance Issues for guidance on additional information to provide.
- If you are reporting an issue with Stardog Cluster, please see Cluster Issues for guidance on additional information to provide.
Creating a Diagnostics Report
The Stardog Admin CLI command diagnostics report can be used to compile diagnostics information from a single Stardog node deployment into a zip file which can then be sent to our support team.
This section only pertains to those who are troubleshooting a single node Stardog deployment. See Cluster Issues for information on creating a diagnostics report for a Stardog Cluster.
To create a Stardog diagnostics report:
stardog-admin diagnostics report --output /path/to/stardog-diagnostics.zip
- If the
--output/-ooption is omitted, a file with an autogenerated name (e.g.stardog-report_<date>.zip) will be created in the directory this command was executed from.
Requesting a Diagnostics Report from a Remote Server
Stardog can be configured to allow remote clients the ability to request a diagnostics report from the server. The property diagnostics.allowIP can be added to the server’s stardog.properties file to allow the IP addresses specified to request a diagnostics report from the server:
diagnostics.allowIP=98.231.199.129
A salient point here is that any remote client requesting a diagnostics report should have superuser privileges.
Stardog must be restarted after modifying the stardog.properties file in order for the changes to takes effect.
After Stardog has been configured to allow remote clients to request a diagnostics report from itself, the client can execute the following command to obtain the diagnostics report remotely:
stardog-admin --server http://remote-server.com:5820 diagnostics report --remote -o /path/to/stardog-diagnostics.zip
Query Performance Issues
When reporting a query performance issue, please include the following information:
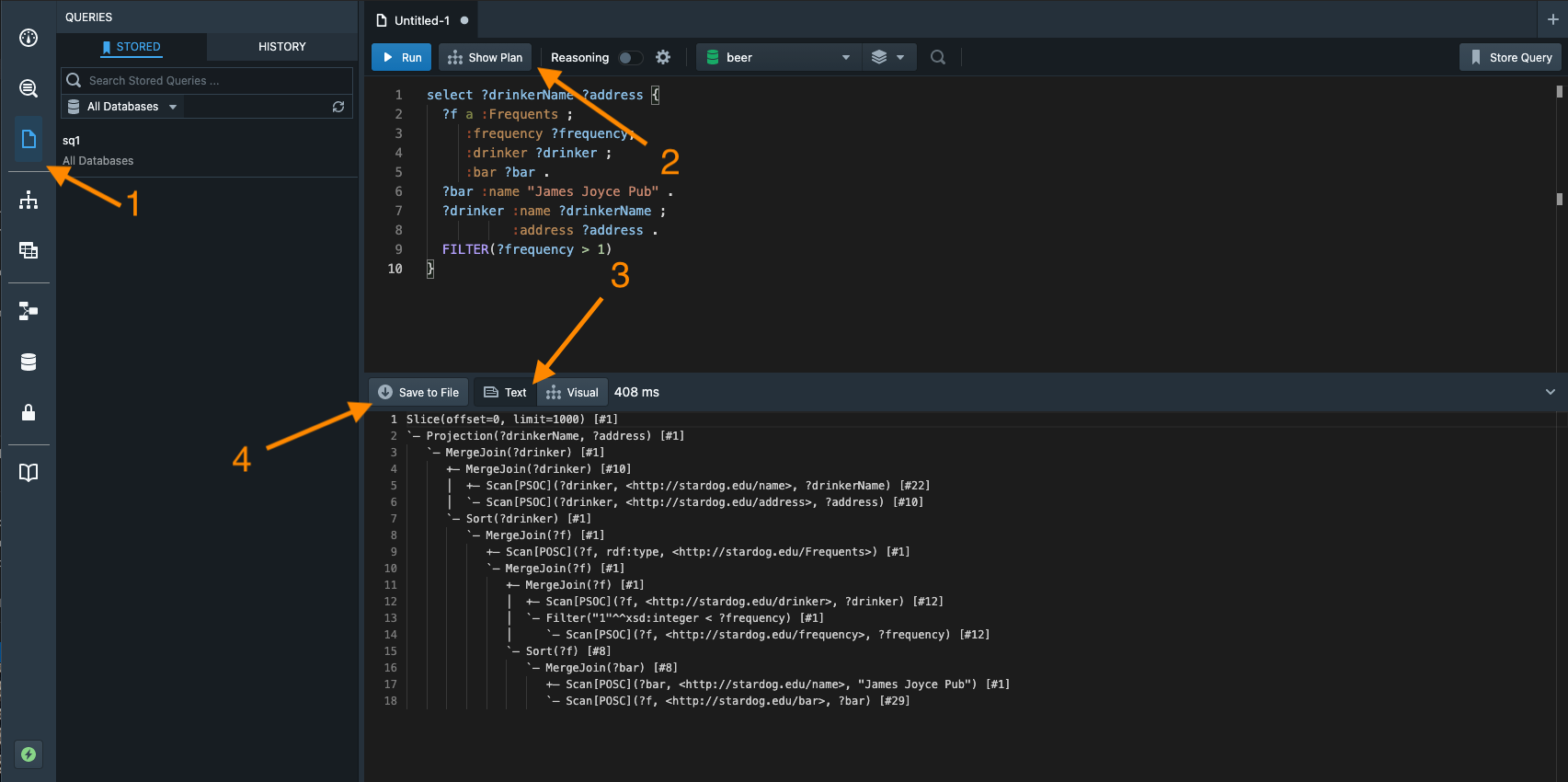
- The query and its associated query plan. Please always copy the plain text version of the plan into an attachment and do not take screenshots of visual plans in Stardog Studio. To obtain a query plan:
-
Use the
query explainCLI command.stardog query explain myDatabase "SELECT ?title WHERE { <http://example.org/book/book1> <http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/title> ?title . }"You can optionally save the query into a file and provide the path of the file to the command like so:
stardog query explain myDatabase ~/queries/myQuery.rq -
Go the “Workspace” tab in Studio and open up your query in the editor. Click on the “Show Plan” button. By default, the visual studio query plan will be shown. Please toggle the query plan display options from “Visual” to “Text”. From here, you can either click the “Save to File” button to save the query plan to a file or just copy the text to a plain text file.
- If you are reporting a regression in query performance between versions, please share the query plans for the problematic query from both versions.
- If the query is a SPARQL Update query, the query plan is not very useful because update query planning is done during query execution, not prior to it. Please convert the query to a
CONSTRUCTwhich uses the sameWHEREpattern and the same graph template asINSERT(orDELETE) and include the query plan for that. - If you have a long running query or a query that fails to terminate after manually killing it, it’s best to additionally collect metrics while the query is running or “stuck” in the “Terminated” state. To collect server metrics, execute the
server metricsStardog Admin CLI command with the--threadsflag:
stardog-admin server metrics --threads > server_metrics.out
- If the query is only slow when reasoning is enabled, it’s helpful to share the schema, if possible. Your reasoning schema can be exported using the CLI with the
reasoning schemacommand:
stardog reasoning schema -f pretty_turtle myDatabase > reasoning_schema.ttl
The above command can be modified to export the reasoning schema if it resides in a named graph and not the default graph. See the reasoning schema manual page for more examples.
Cluster Issues
To gather logs and system information in a cluster generate the cluster diagnostics zip with stardog-admin cluster diagnostics-report
This command requires a running cluster to gather the report from any participating nodes. If there are nodes that have been expelled from the cluster you must gather this information manually.
In addition to the information described in Reporting an Issue and the cluster diagnostics zip please also try to gather the following:
- ZooKeeper logs from all ZooKeeper nodes
- Description of how Stardog was installed: zip, packages, Docker, helm charts in Kubernetes
- A list of any running queries and query plans (if applicable)
- A description of what actions you were performing around the time errors started occurring
- Output of
zk info:
stardog-admin zk info
If Stardog is running in Kubernetes, please also provide:
- The command being used to deploy Stardog (e.g.,
helm install) and any custom values defined invalues.yaml - Output of the following commands:
kubectl -n <your namespace> get pods
kubectl -n <your namespace> describe pod <pod> # for each Stardog and ZooKeeper pod
kubectl -n <your namespace> get events --sort-by=.metadata.creationTimestamp
Logs
Stardog Platform
The logs for the Stardog platform are stored in the stardog.log file within your STARDOG_HOME directory. See the section on Logging for additional information.
Stardog Applications
For Stardog’s applications, log messages are written to the browser’s console. If reaching out for support, please share recent browser console messages.