Using Unstructured Data with Voicebox
A comprehensive guide for developers to integrate and manage unstructured data with Stardog Voicebox using the BITES (Blob Indexing and Text Enrichment with Semantics) system.
Page Contents
- Overview
- Quick Start
- Prerequisites and Requirements
- API Reference
- Document Indexing Pipeline
- Job Configuration
- Querying Indexed Documents
- Deployment
- Deployment Architecture
- Prerequisites
- Step 1: Install Spark Operator
- Step 2: Configure Docker Image Access
- Step 3: Configure vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
- Step 4: Configure voicebox-service
- Step 5: Configure RBAC
- Step 6: Configure Networking
- Step 7: Deploy voicebox-service
- Cluster Sizing Recommendations
- Logging
- Troubleshooting
- Docker Image Availability
- Additional Resources
Overview
BITES (Blob Indexing and Text Enrichment with Semantics) is Stardog Voicebox’s unstructured data support system. It enables ingestion of documents from various cloud storage providers and local sources, allowing users to query both structured and unstructured data through Voicebox’s conversational AI interface.
What is BITES?
BITES provides an API-first approach to indexing and querying unstructured documents alongside your structured data in Stardog. The system leverages Apache Spark for distributed processing and integrates with your existing Kubernetes infrastructure.
Supported Data Sources
- Google Drive - Cloud document storage
- Microsoft OneDrive - Personal and business cloud storage
- Microsoft SharePoint - Enterprise document management (Document Library only)
- Dropbox - Cloud file storage
- Amazon S3 - Object storage
- Local Storage - File system accessible from Kubernetes environment
Supported Document Formats
- Microsoft Word (DOCX)
The system currently supports parsing and indexing of textual and tabular data. Image parsing within documents is planned for a future release.
Key Capabilities
- Data Ingestion: Automated ingestion from multiple data source types
- Unified Querying: Query both structured and unstructured data through a single Voicebox interface
- API-First Design: All functionality accessible through Launchpad’s public APIs
- Distributed Processing: Spark-based job execution in your Kubernetes environment
- Job Management: Full lifecycle management including status monitoring and cancellation
- Vector Indexing: Document chunks indexed in Stardog’s vector store for semantic search
- Knowledge Graph Creation: Optional extraction of entities and relationships from documents to build knowledge graphs
Beta Features: Information extraction and knowledge graph creation are currently in Beta. These features enable extraction of structured entities and relationships from unstructured text.
Architecture Overview

System Flow:
- User initiates data ingestion and indexing via Launchpad’s public APIs
- Voicebox service creates and submits a Spark job to the Kubernetes cluster
- Spark job processes documents: reads from source, parses content, chunks text
- Processed chunks are indexed in Stardog’s vector store
- (Optional) If information extraction is enabled, entities and relationships are extracted and stored as a knowledge graph
- User queries Voicebox, which retrieves answers from both structured data and indexed documents
Quick Start
This section provides a fast-track setup example for indexing Google Drive documents.
Prerequisites Checklist
- Kubernetes cluster with Spark Operator installed
- Voicebox service and voicebox-bites containers running
- Launchpad API key generated
- Data source credentials configured
- Stardog connection configured
5-Minute Setup (Google Drive)
- Configure Google Drive (see Google Drive Configuration)
- Get API Key from Launchpad → “Manage API Keys”
- Base64 encode your Google service account JSON
- Call the API (see example below)
- Monitor job using the job_id returned
# Example: Initiate indexing job
curl -X POST "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"directory": "your-folder-id",
"credentials": "BASE64_ENCODED_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON",
"job_name": "my-indexing-job",
"job_config": {
"document_store_type": "google_drive",
"extract_information": false
}
}'
Prerequisites and Requirements
Data Source Configuration
Before using BITES APIs, you must configure access credentials for your data sources. Each provider requires specific setup steps.
Google Drive
Setup Steps:
- Navigate to Google Cloud Console
- Create a new project or select an existing one
- Enable the Google Drive API
- Go to “APIs & Services” → “OAuth consent screen” and configure
- Go to “Credentials” → “Create Credentials” → “Service Account”
- Create a Service Account with appropriate permissions
- In the Service Account details, go to the “Keys” tab
- Click “Add Key” → “Create new key” → “JSON”
- Download the JSON key file
Required API Scope:
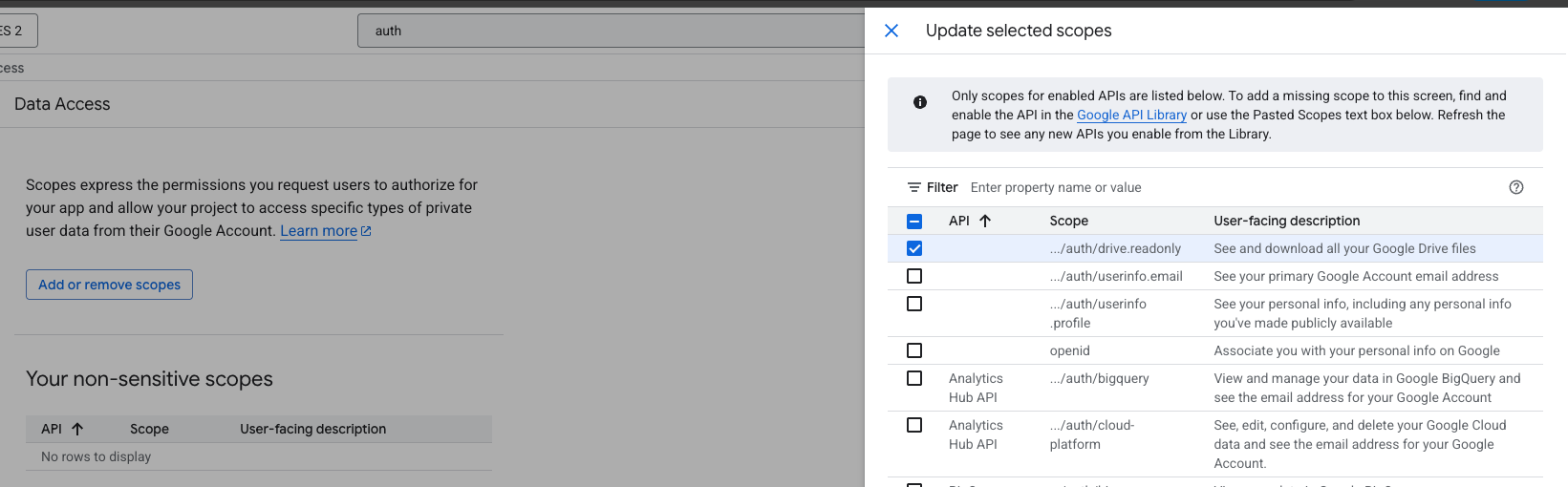
Add the following scope: https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly
IAM Configuration:
Service Account JSON Structure:
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "your-project-id",
"private_key_id": "your-private-key-id",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\nYOUR_PRIVATE_KEY\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "your-service-account@your-project.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "your-client-id",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/your-service-account",
"universe_domain": "googleapis.com"
}
Security Note: Store service account credentials securely. Never commit them to version control. Use environment variables or secret management systems.
Sharing Documents:
To allow the service account to access specific folders:
- Copy the
client_emailfrom the service account JSON - Share the Google Drive folder with this email address
- Grant appropriate permissions (Viewer for read-only access)
OneDrive
Setup Steps:
- Go to Azure Portal
- Navigate to “Azure Active Directory” → “App registrations”
- Click “New registration”
- Provide a name and configure redirect URIs if needed
- After registration, note the Application (client) ID and Directory (tenant) ID from the overview page
- Go to “Certificates & Secrets” → “Client secrets” → “New client secret”
- Copy the secret value (not the secret ID)
Required Microsoft Graph Permissions:
- Files.Read
- Files.ReadAll (Delegated)
- Files.ReadAll (Application)
- offline_access (Delegated)
- openid (Delegated)
- Sites.ReadAll (Delegated)
- User.Read (Delegated)
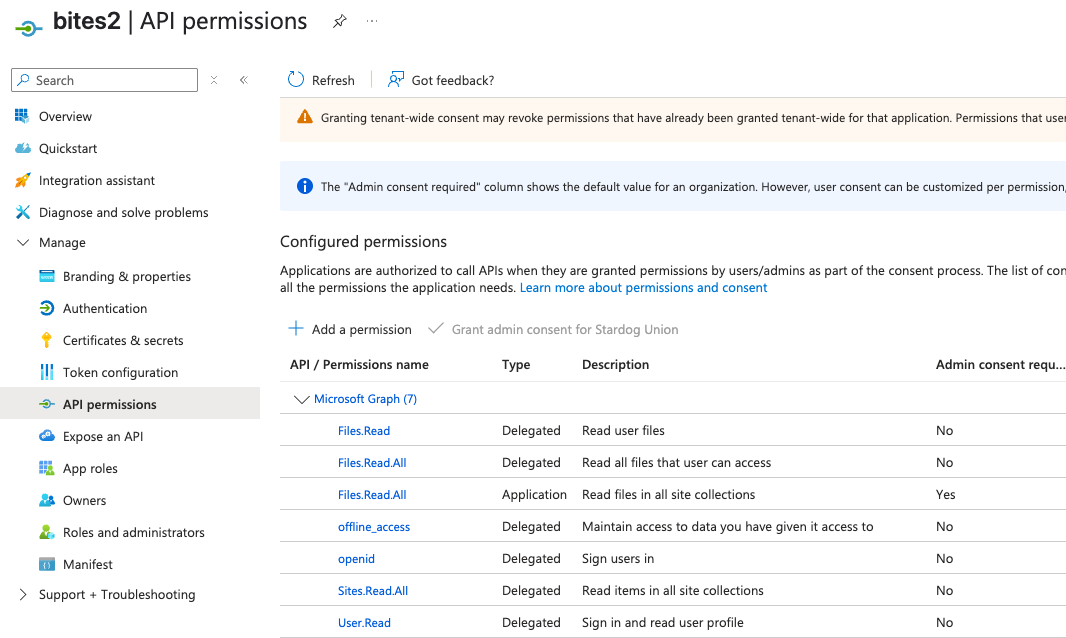
Grant Admin Consent:
After adding permissions, click “Grant admin consent” to approve them for your organization.
Secret Configuration:
Credentials JSON Structure:
{
"tenant_id": "your-tenant-id",
"client_id": "your-client-id",
"client_secret": "your-client-secret"
}
Microsoft SharePoint
Only Document Library is currently supported for SharePoint.
Setup Steps:
- Create an Entra ID (Azure Active Directory) on the Azure Portal
- Create and register an application in Entra ID
- Note the Application (client) ID from the overview page
- Go to “Certificates & Secrets” and create a new client secret
- Copy the secret value
Required Microsoft Graph Permissions:
- Files.Read
- Files.ReadAll (Delegated)
- Sites.ReadAll (Delegated)
- Sites.ReadAll (Application)
- User.Read (Delegated)
Required SharePoint Permissions:
- AllSites.Read (Delegated)
- MyFiles.Read (Delegated)
- Sites.Read.All (Application)
- Sites.Select.All (Application)
- User.Read.All (Application)
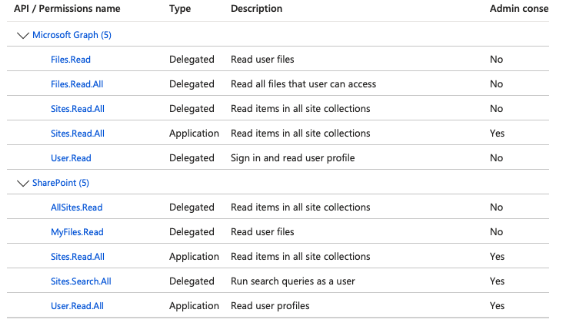
Some permissions require M365 administrator approval. Contact your administrator to grant these permissions.
Credentials JSON Structure:
{
"tenant_id": "your-tenant-id",
"client_id": "your-client-id",
"client_secret": "your-client-secret"
}
Additional Required Information:
When calling the indexing API for SharePoint, you must also provide:
host_name: Your SharePoint host (e.g., “yourcompany.sharepoint.com”)site_id: The SharePoint site IDlibrary_name: The document library name
Dropbox
Setup Steps:
- Go to Dropbox App Console
- Click “Create app”
- Choose “Scoped access” and “Full Dropbox” or “App folder”
- Provide an app name
- Go to the “Permissions” tab and enable required scopes:
files.metadata.readfiles.content.read
- Note your App key and App secret
OAuth Authorization Flow:
- In your browser, visit:
https://www.dropbox.com/oauth2/authorize?client_id=<APP_KEY>&token_access_type=offline&response_type=codeReplace
<APP_KEY>with your actual app key. -
Log in to Dropbox and approve the app
-
Copy the authorization code from the redirect URL
- Exchange the authorization code for tokens:
curl -X POST https://api.dropboxapi.com/oauth2/token \ -d code=<AUTHORIZATION_CODE> \ -d grant_type=authorization_code \ -d client_id=<APP_KEY> \ -d client_secret=<APP_SECRET> - The response contains:
access_token: Current access tokenrefresh_token: Long-lived token for obtaining new access tokens
Credentials JSON Structure:
{
"access_token": "your-current-access-token",
"refresh_token": "your-refresh-token",
"client_id": "your-app-key",
"client_secret": "your-app-secret"
}
The BITES connector automatically handles token refresh. If the access token expires, it uses the refresh token to obtain a new one.
Amazon S3
BITES supports two authentication options for S3: IAM roles (recommended) and access keys.
Option 1: IAM Roles (Recommended for AWS-hosted applications)
- Go to AWS Management Console → IAM
- Click “Roles” → “Create role”
- Select the service that will assume this role (e.g., EC2, EKS)
- Attach permissions policies:
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess(for read-only access)- Or create a custom policy with minimal required permissions
- Review and create the role
- Attach this role to your Kubernetes nodes or pods
Option 2: Access Key and Secret Key
- Go to AWS Management Console → IAM
- Click “Users” → “Add user”
- Provide a username and select “Programmatic access”
- Attach permissions policies (e.g.,
AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess) - Complete user creation
- Download the CSV file containing the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key
Security Best Practice: Use IAM roles when possible. If using access keys, rotate them regularly and store them securely.
Required S3 Permissions:
Your IAM role or user must have the following permissions on the target bucket:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:GetObjectVersion",
"s3:ListBucketVersions"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name/*"
]
}
]
}
Bucket Configuration:
- Open AWS Console and navigate to S3
- Select your bucket
- Go to “Permissions” tab
- Ensure the IAM role/user has the required permissions listed above
Credentials JSON Structure:
{
"aws_access_key_id": "your-access-key",
"aws_secret_access_key": "your-secret-key",
"region_name": "us-east-1",
"use_iam_role": false
}
For IAM Role Authentication:
{
"region_name": "us-east-1",
"use_iam_role": true
}
Additional Required Information:
When calling the indexing API for S3, you must also provide:
bucket: The S3 bucket name in theextra_argsparameter
Local Storage
Local storage allows indexing of files directly accessible from the Kubernetes environment.
Requirements:
- The directory must be accessible from the Spark executors
- Use Kubernetes volumes (PersistentVolumes, ConfigMaps, or mounted storage)
- Ensure appropriate read permissions
Credentials:
No credentials are required for local storage. Pass an empty JSON object (base64 encoded):
{}
Directory Path:
Provide the absolute path to the directory within the container filesystem (e.g., /mnt/data/documents).
API Key Generation
All BITES APIs require authentication using a Launchpad API key.
Steps to Generate API Key:
- Log in to Launchpad
- Navigate to “Manage API Keys”
- Click “Create API Key”
- Provide a name and select the database
- Copy and securely store the API key
API keys provide full access to your Voicebox instance. Store them securely and never expose them in client-side code or public repositories.
Using the API Key:
Include the API key in the Authorization header of all API requests:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Stardog Connection Configuration
BITES jobs need to connect to Stardog to index documents. Two authentication options are supported.
Option 1: Stardog JWT Token
Prerequisites:
- A valid JWT token issued by your Stardog server (the same server provided as the
endpointin the API)
How it Works:
Obtain a JWT token from the Stardog server and pass it via the X-SD-Auth-Token header when calling the BITES API. The token is forwarded to the Spark job for authenticating against Stardog during indexing.
Token Expiry: Set token expiry based on the expected job duration. For very long-running jobs, consider breaking the work into smaller batches to avoid creating tokens with very long expiration times.
Option 2: SSO Authentication (Azure/Okta/Ping)
Prerequisites:
- SSO provider configured and integrated with Stardog
- Valid refresh token from SSO provider
- SSO provider client ID
How it Works:
When you initiate a job, the system calls the SSO provider to fetch an access token using the refresh token. This access token is then passed to the Spark job.
Configuration:
When calling the indexing API, provide:
sso_provider_client_id: Your SSO provider’s client IDrefresh_token: A valid refresh token from your SSO provider
LLM Provider Configuration
If you plan to use information extraction (extract_information: true), you must configure environment variables for your LLM provider. These variables must be available on both the driver and executor nodes.
Required Environment Variables by Provider
AWS Bedrock
env:
- name: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID
value: "your-aws-access-key-id"
- name: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
value: "your-aws-secret-access-key"
- name: AWS_REGION
value: "us-east-1"
For AWS Bedrock, ensure your IAM user/role has bedrock:InvokeModel permission for the models you plan to use.
Fireworks AI
env:
- name: FIREWORKS_API_KEY
value: "your-fireworks-api-key"
OpenAI
env:
- name: OPENAI_API_KEY
value: "your-openai-api-key"
Azure OpenAI
env:
- name: AZURE_OPENAI_API_KEY
value: "your-azure-openai-key"
- name: AZURE_OPENAI_ENDPOINT
value: "https://your-resource.openai.azure.com/"
Configuring Environment Variables in Kubernetes
Option 1: Using Kubernetes Secrets (Recommended). Then reference the secret in vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml.
Option 2: Direct Environment Variables (Not Recommended for Production)
Deployment Prerequisites
Before running indexing jobs, ensure your Kubernetes environment is properly configured.
Required Components:
- Kubernetes cluster (version 1.19+)
- Spark Operator installed in the cluster
voicebox-bitesDocker image accessiblevoicebox-servicerunning and configured- Network connectivity between Launchpad, voicebox-service, and voicebox-bites
See the Deployment section for detailed setup instructions.
API Reference
All BITES functionality is accessed through RESTful APIs. This section provides complete API documentation with examples.
Authentication
All API requests must include an Authorization header with your Launchpad API key:
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Base URL
https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites
Replace your-launchpad-url with your actual Launchpad instance URL.
API Endpoints Overview
| Endpoint | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
/jobs | POST | Initiate a new indexing job |
/jobs/{job_id} | GET | Get the status of a job |
/jobs/{job_id}/cancel | POST | Cancel a running job |
Initiate Indexing Job
Creates and starts a new indexing job in the Spark environment.
Endpoint
POST /api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs
Request Headers
Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY
Content-Type: application/json
Request Body Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| database | string | Yes | Stardog database name where indexing output (vector chunks, knowledge graphs) will be stored |
| endpoint | string | Yes | Stardog endpoint URL to connect to (e.g., https://your-stardog-instance:5820) |
| model | string | No | Model/ontology name in Stardog (e.g., my_org:c360). When information extraction is enabled, this ontology defines the entity types and relationships that the system will extract |
| directory | string | Yes | Directory location or ID. For Google Drive: folder ID; OneDrive: folder path; Local: absolute path |
| credentials | string | Yes | Base64-encoded JSON containing data source credentials. See Data Source Configuration for format |
| job_name | string | Yes | Unique name for the job (used for tracking and management) |
| job_namespace | string | No | Kubernetes namespace for the job. Defaults to namespace in vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml |
| batch_size | integer | No | Number of chunks to commit at once. Default: 1000. Increase for better performance, decrease if memory constrained |
| job_config | object | Yes | Configuration controlling scalability and functionality. See Job Configuration |
| sso_provider_client_id | string | Conditional | Required for SSO authentication. SSO provider’s client ID |
| refresh_token | string | Conditional | Required for SSO authentication. Valid refresh token from SSO provider |
| extra_args | object | No | Additional arguments specific to data source type. See below |
Extra Args by Data Source:
| Data Source | Extra Args Required | Example |
|---|---|---|
| OneDrive | one_drive_id | {"one_drive_id": "b!drive_id"} |
| SharePoint | host_name, site_id, library_name | {"host_name": "company.sharepoint.com", "site_id": "site-id", "library_name": "Documents"} |
| S3 | bucket, prefix | {"bucket": "my-documents-bucket", "prefix: "S3 path" } |
| Google Drive | None | - |
| Dropbox | None | - |
| Local | None | - |
Credentials Format by Data Source
Before passing to the API, base64-encode the JSON credentials. See Data Source Configuration for the required JSON structure for each provider.
Minimal Request Example
curl -X POST "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"database": "my_database",
"endpoint": "https://your-stardog-instance:5820",
"directory": "1A2B3C4D5E6F7G8H9I",
"credentials": "eyJ0eXBlIjoic2VydmljZV9hY2NvdW50IiwicHJvamVjdF9pZCI6InlvdXItcHJvamVjdCJ9",
"job_name": "index-google-drive-docs",
"job_config": {
"document_store_type": "google_drive",
"extract_information": false
}
}'
Complete Request Example with All Options
curl -X POST "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"database": "my_database",
"endpoint": "https://your-stardog-instance:5820",
"model": "my_org:c360",
"directory": "b!AbCdEf123456",
"credentials": "eyJ0ZW5hbnRfaWQiOiJ5b3VyLXRlbmFudC1pZCIsImNsaWVudF9pZCI6InlvdXItY2xpZW50LWlkIiwiY2xpZW50X3NlY3JldCI6InlvdXItc2VjcmV0In0=",
"job_name": "onedrive-quarterly-reports",
"job_namespace": "voicebox-production",
"batch_size": 2000,
"sso_provider_client_id": "your-sso-client-id",
"refresh_token": "your-refresh-token",
"extra_args": {
"one_drive_id": "b!AbCdEf123456"
},
"job_config": {
"list_file_parallelism": 10,
"content_reader_parallelism": 20,
"content_indexer_parallelism": 10,
"document_store_type": "onedrive",
"extract_information": true,
"store_list_file_config": {
"page_size": 100,
"recursive": true,
"document_types": ["document", "pdf"]
},
"store_content_loader_config": {
"num_retries": 3,
"store_loader_kwargs": {}
},
"document_loader_config": {
"pdf": {
"chunk_size": 1000,
"chunking_enabled": true,
"chunk_separator": ["\\n\\n", "\\n", ". ", " ", ""],
"chunk_overlap": 200
},
"document": {
"chunk_size": 1000,
"chunking_enabled": true,
"chunk_separator": ["\\n\\n", "\\n", ". ", " ", ""],
"chunk_overlap": 200
}
},
"information_extraction_config": [
{
"task_type": "information_extraction",
"extractor_type": "llm",
"llm_config": {
"max_tokens": 8192,
"temperature": 0.0,
"repetition_penalty": 1.0,
"top_p": 0.7,
"top_k": 50,
"stop": ["---", "</output_format>"],
"llm_name": "us.meta.llama4-maverick-17b-instruct-v1:0",
"llm_provider": "bedrock",
"context_window": 128000
},
"num_retries": 3,
"query_timeout": 50000
}
]
}
}'
Response
Success Response (HTTP 200):
{
"job_id": "spark-app-1234567890-abcdef",
"error": null
}
Error Response (HTTP 400/500):
{
"job_id": null,
"error": "Failed to create job: Invalid credentials format"
}
Response Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| job_id | string or null | Unique identifier for the created job. Use this to check status or cancel the job |
| error | string or null | Error message if job creation failed, null otherwise |
Get Job Status
Retrieves the current status of an indexing job.
Endpoint
GET /api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs/{job_id}
Path Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| job_id | string | Yes | Job ID returned when the job was created |
Query Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| job_namespace | string | No | Kubernetes namespace of the job. Defaults to namespace in vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml |
Request Example
curl -X GET "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs/spark-app-1234567890-abcdef" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"
Response
Success Response (HTTP 200):
{
"status_code": "RUNNING",
"status": "Job is processing documents. Completed 45 of 100 files."
}
Job Not Found (HTTP 404):
{
"status_code": "UNKNOWN",
"status": "Job not found"
}
Response Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| status_code | string | Current state of the job. See status codes below |
| status | string | Human-readable status message with additional details |
Status Codes
| Status Code | Description |
|---|---|
| NEW | Job created but not yet submitted to Spark |
| SUBMITTED | Job submitted to Spark cluster, waiting for resources |
| RUNNING | Job actively processing documents |
| PENDING_RERUN | Job failed and is waiting to be retried |
| INVALIDATING | Job is being invalidated |
| SUCCEEDING | Job is in the process of completing successfully |
| COMPLETED | Job finished successfully |
| ERROR | Job encountered a non-recoverable error |
| FAILING | Job is in the process of failing |
| FAILED | Job failed |
| UNKNOWN | Job status cannot be determined (job may not exist) |
Polling Recommendations
- Poll every 10-30 seconds for jobs expected to complete quickly
- Poll every 1-5 minutes for long-running jobs
- Stop polling when status is
COMPLETED,FAILED, orERROR
Cancel Job
Cancels a running or pending indexing job.
Endpoint
POST /api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs/{job_id}/cancel
Path Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| job_id | string | Yes | Job ID of the job to cancel |
Request Body Parameters
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| job_name | string | Yes | Name of the job to cancel (must match the name used when creating the job) |
| job_namespace | string | No | Kubernetes namespace of the job. Defaults to namespace in vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml |
Request Example
curl -X POST "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs/spark-app-1234567890-abcdef/cancel" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"job_name": "index-google-drive-docs"
}'
Response
Success Response (HTTP 200):
{
"success": true,
"error": null
}
Error Response (HTTP 400/500):
{
"success": false,
"error": "Job not found or already completed"
}
Response Fields
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| success | boolean | True if the job was successfully canceled, false otherwise |
| error | string or null | Error message if cancellation failed, null otherwise |
Canceling a job may take a few moments. The Spark operator will gracefully terminate the running executors. Already indexed documents will remain in Stardog.
Document Indexing Pipeline
Understanding the indexing pipeline helps you configure jobs effectively and troubleshoot issues.
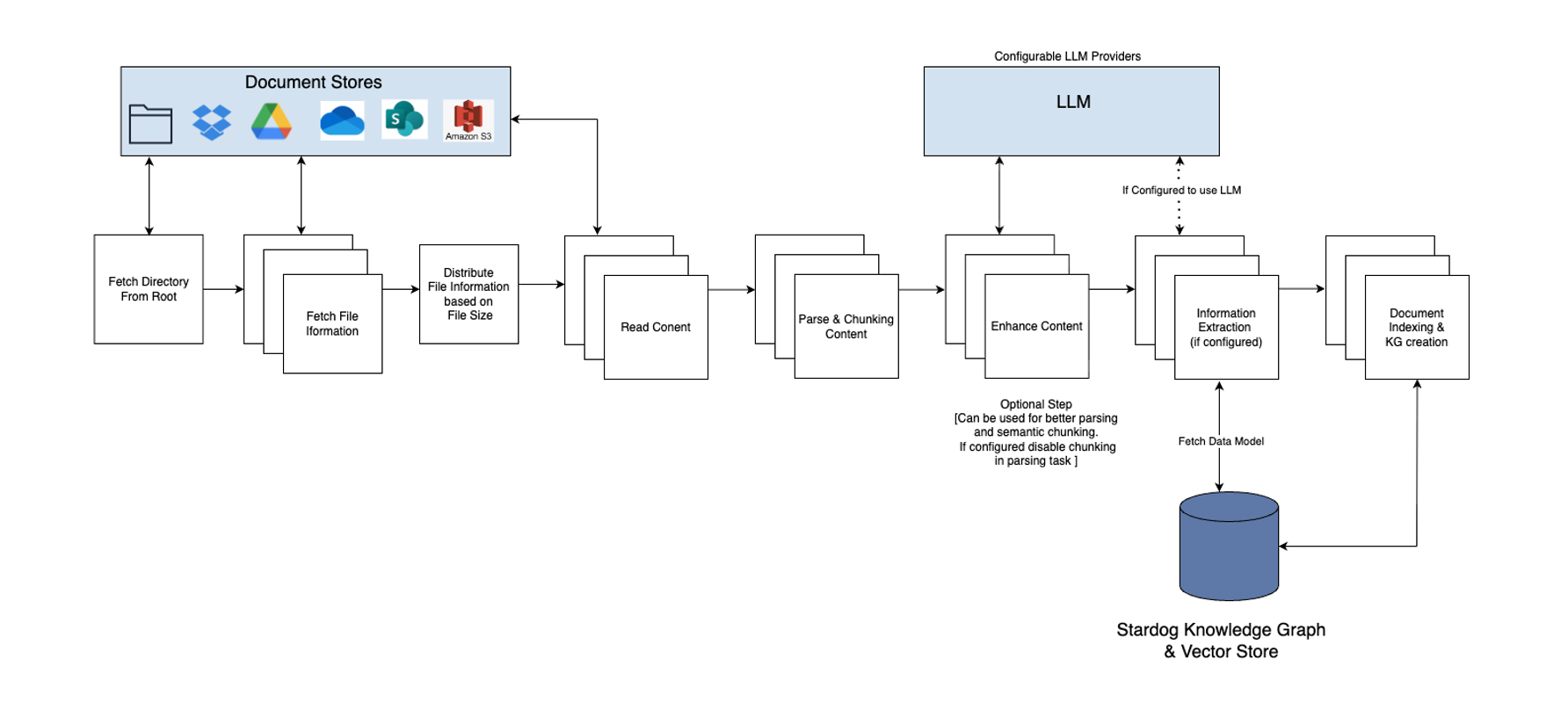
Pipeline Stages
1. List Directories
Purpose: Enumerate all directories within the specified location.
Configuration: Controlled by list_file_parallelism and recursive settings.
Output: List of directories to scan for files.
2. List Supported Files
Purpose: Identify all supported document types (PDF, DOCX) within the directories.
Configuration: Filtered by document_types in store_list_file_config.
Output: List of file paths/IDs with metadata (size, modification date, etc.).
3. Fetch Content and Metadata
Purpose: Download file content from the data source and extract metadata.
Configuration: Controlled by content_reader_parallelism. Retries configured via num_retries.
Metadata Captured:
- File name and path
- Creation and modification dates
- Author information (if available)
- File size
- MIME type
Output: Raw file content and associated metadata.
4. Parse and Chunk Content
Purpose: Extract text from documents and split into manageable chunks.
Parsing:
- PDF: Text and Table extraction from PDF files
- DOCX: Text and table extraction from Word documents
Chunking:
- Split text based on
chunk_sizeandchunk_separator - Apply
chunk_overlapto preserve context between chunks - Maintain metadata association with each chunk
Configuration: Controlled by document_loader_config.
Output: Array of text chunks with metadata.
5. Information Extraction (Optional)
Purpose: Extract structured entities and relationships to build a knowledge graph.
When to Use:
- You want to build a knowledge graph from unstructured documents
- Need to identify entities (people, organizations, locations) and their relationships
- Want to enable graph-based queries alongside vector search
Process:
- LLM analyzes each chunk to identify entities and relationships
- Extracts triples in RDF format (subject-predicate-object)
- Optionally resolves entities within each document
Configuration: Set extract_information: true and configure information_extraction_config.
Entity resolution operates at the document level. Entities are resolved and linked within each document’s context, not across the entire dataset.
Output: RDF triples representing extracted knowledge.
Cost Consideration: This step makes additional LLM API calls per chunk, significantly increasing processing time and cost.
6. Index Chunks
Purpose: Store processed chunks and knowledge graph in Stardog.
Indexing Operations:
- Vector Indexing: Chunks are embedded and stored in Stardog’s vector store
- Metadata Indexing: File metadata stored for filtering and source attribution
- Knowledge Graph Storage: Extracted triples stored in specified graph (if information extraction enabled)
Configuration: Controlled by content_indexer_parallelism and batch_size.
Output: Indexed and searchable content in Stardog.
Pipeline Performance Considerations
Bottlenecks:
- Data Source API Limits: Google Drive, OneDrive have rate limits
- Network Bandwidth: Large files take time to download
- LLM Processing: Content enhancement and information extraction are slow
- Stardog Ingestion: High parallelism can overload Stardog
Optimization Tips:
- Start with conservative parallelism settings
- Monitor data source rate limits
- Use content enhancement and information extraction only when necessary
- Increase
batch_sizefor better ingestion throughput - Scale Stardog appropriately for your indexing load
Job Configuration
The job_config parameter controls both scalability and functionality of the indexing pipeline. Most options have sensible defaults — you only need to specify what you want to customize.
Minimal Configuration
{
"document_store_type": "google_drive"
}
This uses all defaults: PDF and DOCX document types, recursive file listing, no information extraction.
Complete Configuration Reference
Below is a complete configuration showing all available options with their defaults:
{
"list_file_parallelism": 5,
"content_reader_parallelism": 10,
"content_indexer_parallelism": 5,
"document_store_type": "google_drive",
"extract_information": false,
"store_list_file_config": {
"page_size": 100,
"recursive": true,
"document_types": ["document", "pdf"],
"loader_kwargs": {}
},
"store_content_loader_config": {
"num_retries": 2,
"store_loader_kwargs": {}
},
"document_loader_config": {
"pdf": {
"chunk_size": 1000,
"chunking_enabled": true,
"chunk_separator": ["\n\n", "\n", ". ", " ", ""],
"chunk_overlap": 0,
"loader_type": "py_pdf",
"loader_kwargs": {}
},
"document": {
"chunk_size": 1000,
"chunking_enabled": true,
"chunk_separator": ["\n\n", "\n", ". ", " ", ""],
"chunk_overlap": 0,
"loader_type": "DocxLoader",
"loader_kwargs": {}
}
},
"information_extraction_config": [{
"task_type": "information_extraction",
"extractor_type": "llm",
"kwargs": {},
"num_retries": 3,
"query_timeout": 50000,
"llm_config": {
"max_tokens": 8192,
"temperature": 0,
"context_window": 128000,
"stop": ["---", "</output_format>"]
}
}]
}
Performance Tuning
| Parameter | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
list_file_parallelism | 5 | Parallel tasks for discovering files from document stores |
content_reader_parallelism | 10 | Parallel tasks for reading and parsing documents (most impactful setting) |
content_indexer_parallelism | 5 | Parallel tasks for indexing into Stardog vector store |
Higher parallelism increases pressure on data source APIs and Stardog. Monitor for rate limit errors and resource utilization (CPU, memory, disk I/O).
Large document sets (10K+ documents):
{
"list_file_parallelism": 10,
"content_reader_parallelism": 50,
"content_indexer_parallelism": 5
}
Memory-constrained environments:
{
"list_file_parallelism": 2,
"content_reader_parallelism": 3,
"content_indexer_parallelism": 2
}
Document Store Type
| Store | document_store_type Value | Auth Required |
|---|---|---|
| Google Drive | google_drive | Service account JSON (base64) |
| Dropbox | dropbox | OAuth token (base64) |
| OneDrive | onedrive | OAuth credentials (base64) |
| SharePoint | sharepoint | OAuth credentials (base64) |
| Amazon S3 | s3 | AWS credentials (base64) |
| Local | local | None |
extract_information
Set to true to enable LLM-based entity and relationship extraction for building a knowledge graph. Default: false.
When enabled, the system extracts entities and relationships based on the ontology defined in the model specified in the API request, storing them as RDF triples in Stardog. The extraction is schema-driven — it does not create new entity types but extracts instances of types defined in your ontology. This increases processing time by 5-20x and incurs additional LLM API costs per chunk. Requires information_extraction_config to be configured with LLM settings.
store_list_file_config
Controls file discovery behavior.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
page_size | integer | 100 | Files fetched per API call (typical range: 50-200) |
recursive | boolean | true | Scan subdirectories |
document_types | array | ["document", "pdf"] | File types to process ("document" = DOCX) |
loader_kwargs | object | {} | Store-specific options |
store_content_loader_config
Controls file content fetching behavior.
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
num_retries | integer | 2 | Retry attempts for failed downloads (2-3 recommended) |
store_loader_kwargs | object | {} | Store-specific options |
For S3 data sources, you can pass streaming_threshold_mb (default: 20) in store_loader_kwargs to control the file size threshold above which S3 objects are streamed rather than downloaded fully into memory.
document_loader_config
Defines parsing and chunking strategy per document type. Configure separately for "pdf" and "document" (DOCX):
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
chunk_size | integer | 1000 | Maximum characters per chunk (300-500 for precision, 800-1200 balanced, 1500-2000 for speed) |
chunking_enabled | boolean | true | Enable text chunking (disable only for very small documents) |
chunk_separator | array | ["\n\n", "\n", ". ", " ", ""] | Priority-ordered separators for splitting text |
chunk_overlap | integer | 0 | Characters to overlap between chunks (100-200 for general, 300-500 for complex documents) |
loader_type | string | varies | Parser type: "py_pdf" for PDFs, "DocxLoader" for DOCX |
loader_kwargs | object | {} | Parser-specific parameters |
You can use different settings for PDFs vs. DOCX:
{
"document_loader_config": {
"pdf": {
"chunk_size": 1200,
"chunk_overlap": 200
},
"document": {
"chunk_size": 800,
"chunk_overlap": 100
}
}
}
information_extraction_config
Configures entity and relationship extraction. Required when extract_information: true.
Task Configuration Fields
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
task_type | string | "information_extraction" | Type of extraction task |
extractor_type | string | "llm" | Extractor implementation: llm, spacy, or nltk (see below) |
kwargs | object | {} | Optional. Advanced IE parameters for fine-tuning (see Advanced IE Configuration) |
llm_config | object | required | LLM model configuration |
num_retries | integer | 3 | Retry attempts for failed operations |
query_timeout | integer | 50000 | Timeout in milliseconds for Stardog queries (schema fetching for LLM IE, search queries for SpaCy/NLTK) |
Extractor Types
llm: LLM-based extraction using configured LLM provider (most flexible, requires LLM config)spacy: SpaCy NER model detects entities, then LLM maps entity types using an internal job-specific cache to minimize LLM callsnltk: NLTK NER (lightweight, no LLM required)
LLM Configuration
| Field | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
max_tokens | integer | 8192 | Maximum tokens in LLM response |
temperature | float | 0.0 | Sampling temperature (0.0 = deterministic) |
context_window | integer | 128000 | Context window size — match to your LLM’s actual window |
stop | array | ["---", "</output_format>"] | Stop sequences for generation |
repetition_penalty | float | 1.0 | Penalty for repeated tokens |
top_p | float | — | Nucleus sampling parameter |
top_k | integer | — | Top-k sampling parameter |
llm_name | string | — | Model identifier (provider-specific) |
llm_provider | string | — | LLM provider identifier |
Contact Stardog support to get the list of currently supported LLM providers and their available models.
Advanced IE Configuration (kwargs)
All kwargs parameters are optional and not required for basic information extraction. The defaults work well for most use cases. Consider tuning these only after running an initial extraction and reviewing the results.
| Key | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
bites_ie_entity_scope | object | {} | Controls IRI uniqueness scope for extracted entities |
bites_ie_instructions | string | "" | Custom domain-specific instructions injected into the IE prompt |
bites_ie_max_chunks_per_llm_call | int | auto | Max sequential chunks clubbed into a single batch per LLM call for IE (auto-calculated from context window) |
bites_ie_schema_sample_count | int | 8 | Number of chunks sampled from a document to estimate schema token usage when building batch sizes based on the context window |
bites_ie_enable_entity_resolution | bool | false | Enable document-level entity resolution |
bites_ie_er_max_entities_per_call | int | 50 | Max entities per entity resolution call |
bites_ie_er_instructions | string | "" | Custom instructions for entity resolution |
Entity Scope
By default, all entities use GLOBAL_SCOPE — the same entity text produces the same IRI across all documents, which means entities are automatically linked across your entire document set. Use DOCUMENT_SCOPE when an entity type is only meaningful within a single document (e.g., “Agreement” or “Contract” where each document has its own distinct instance).
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
GLOBAL_SCOPE | IRIs are globally unique — same entity text produces the same IRI across all documents (default). Best for entities like people, organizations, and locations that span multiple documents |
DOCUMENT_SCOPE | IRIs include document ID suffix — entities are unique per document. Best for document-specific concepts like agreements, contracts, or service terms |
Example:
"bites_ie_entity_scope": {
"GLOBAL_SCOPE": ["Party", "Company"],
"DOCUMENT_SCOPE": ["Agreement", "Service"]
}
Custom IE Instructions
Use bites_ie_instructions to inject domain-specific guidance into the extraction prompt. This helps the LLM focus on the most relevant entities and relationships for your use case.
We recommend an iterative approach: first run extraction on a sample document without custom instructions, review the results, then add instructions to address gaps or improve focus. Instructions can be extensive — from a single sentence to multiple paragraphs covering specific extraction rules, entity definitions, or relationship patterns relevant to your domain.
Example: "Focus on extracting financial terms and party relationships. When encountering contract clauses, extract the clause type, parties involved, and any monetary values or dates mentioned."
Entity Resolution
If your documents contain different text representations of the same real-world entity (e.g., “IBM”, “International Business Machines”, “IBM Corp.”), entity resolution can help. When enabled via bites_ie_enable_entity_resolution: true, the system performs document-level entity resolution to merge these duplicate mentions into unified “golden entities,” reducing redundancy in the knowledge graph.
Entity resolution adds one additional LLM call per document. Only enable this when you expect significant entity duplication in your documents and the merging benefit justifies the additional cost.
Tune with bites_ie_er_max_entities_per_call (default 50) to control batch size. Use bites_ie_er_instructions to provide domain-specific merging guidance — as with bites_ie_instructions, we recommend an iterative approach: run with entity resolution enabled but without custom instructions first, review the merging results, then add instructions to correct any gaps (e.g., rules for when abbreviations should or should not be merged). Instructions can be extensive.
Batch Processing
For information extraction, sequential chunks from a document are clubbed together into batches and sent in a single LLM call. The bites_ie_max_chunks_per_llm_call parameter controls the maximum number of chunks per batch. By default, this is auto-calculated based on the context_window size to maximize throughput. Override manually if you need to reduce the number of LLM calls or manage memory usage.
Complete IE Configuration Example
{
"information_extraction_config": [{
"task_type": "information_extraction",
"extractor_type": "llm",
"kwargs": {
"bites_ie_entity_scope": {
"GLOBAL_SCOPE": ["Party", "Company"],
"DOCUMENT_SCOPE": ["Agreement", "Service"]
},
"bites_ie_instructions": "Focus on extracting financial terms and party relationships.",
"bites_ie_max_chunks_per_llm_call": 5,
"bites_ie_schema_sample_count": 8,
"bites_ie_enable_entity_resolution": true,
"bites_ie_er_max_entities_per_call": 50,
"bites_ie_er_instructions": "Merge entities that refer to the same real-world entity."
},
"num_retries": 3,
"query_timeout": 50000,
"llm_config": {
"max_tokens": 8192,
"temperature": 0,
"context_window": 128000,
"stop": ["---", "</output_format>"],
"llm_name": "us.meta.llama4-maverick-17b-instruct-v1:0",
"llm_provider": "bedrock"
}
}]
}
Information extraction significantly increases processing time and costs due to LLM API calls per chunk. Budget accordingly for large document sets.
Start with default values, monitor performance, and gradually increase parallelism. Always test with a small subset before indexing your entire dataset.
Querying Indexed Documents
Once documents are indexed, you can query them through the Voicebox UI.
Vector Search Queries
Documents indexed without information extraction can be queried using natural language questions.
Example Questions:
- “What are the main points in the Q4 financial report?”
- “Summarize the product requirements document for Project Alpha”
- “What were the action items from the last board meeting?”
Source Attribution
Voicebox provides source attribution for answers derived from indexed documents.
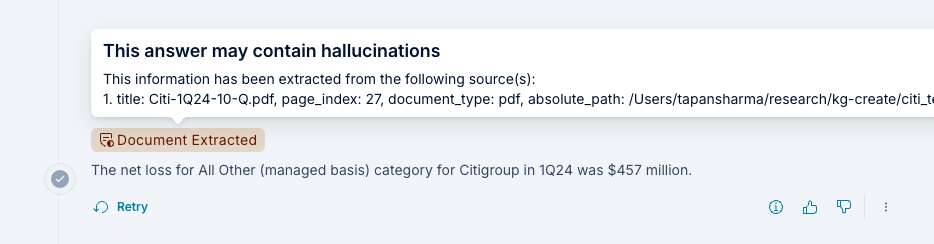
Hover over “Document Extracted” text to see:
- Source file name
- Page number (for PDFs) or section
- Relevance score
- Direct link to original document (if available)
Knowledge Graph Queries
If information extraction was enabled during indexing, you can ask questions that leverage the knowledge graph.
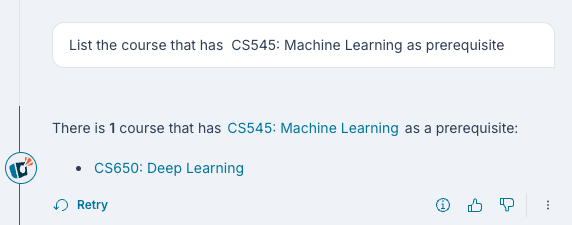
Example Questions:
- “Who are the key people mentioned in relation to Project Apollo?”
- “What organizations are connected to the merger discussion?”
- “Show me all locations mentioned in the travel policy documents”
Knowledge Graph Benefits:
- Discover relationships across multiple documents
- Find entities and their connections
- Ask graph-based questions (e.g., “What connects X and Y?”)
Source Lineage
Knowledge graph queries provide lineage showing which documents contributed to the answer.
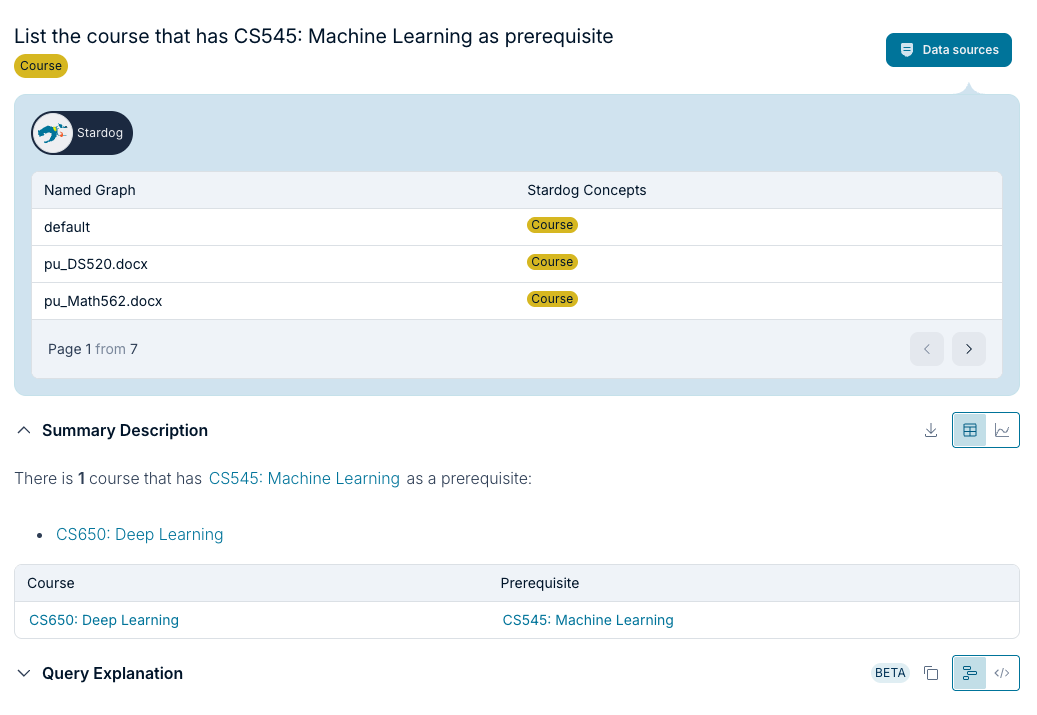
Lineage Information:
- Source documents for each extracted entity
- Document provenance chain
Deployment
This section provides detailed instructions for deploying BITES in your Kubernetes environment.
Deployment Architecture
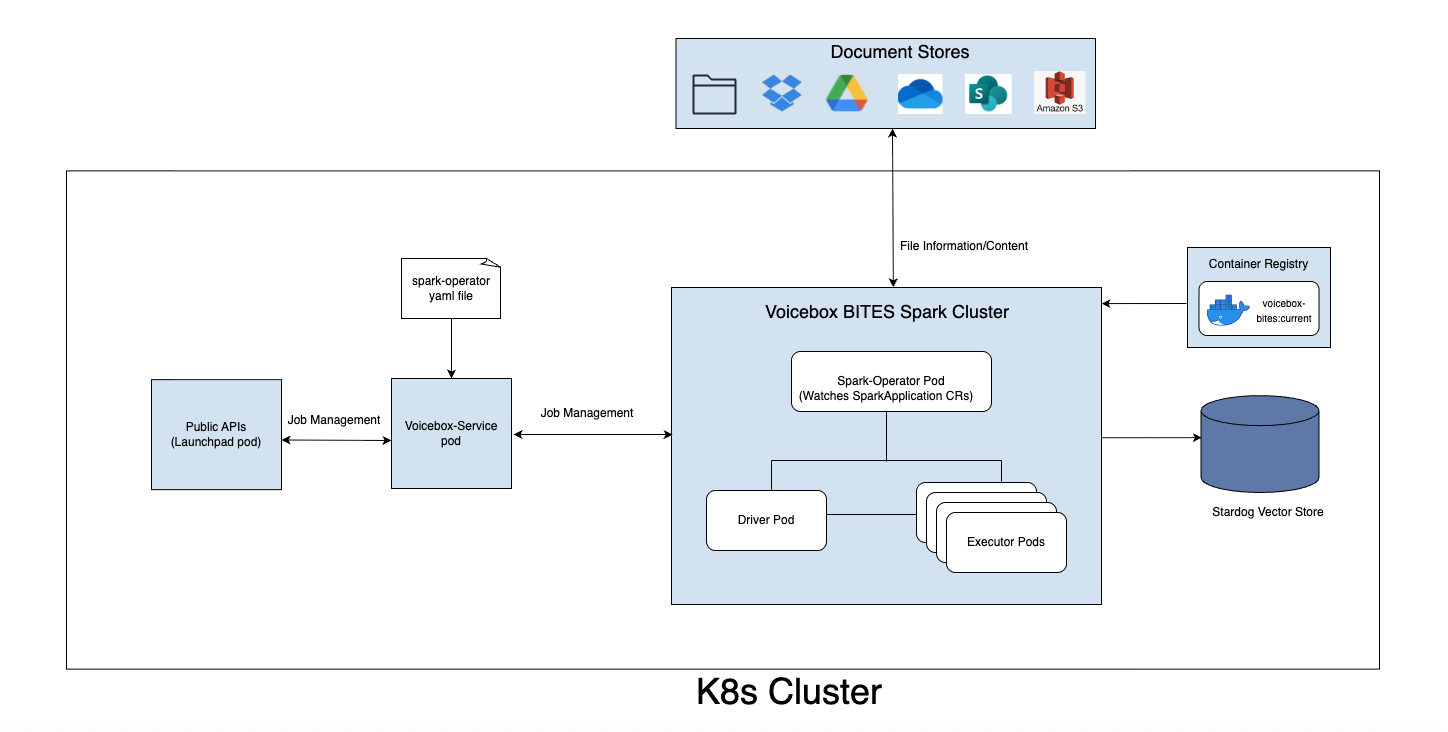
Components:
- Launchpad: Provides APIs and user interface
- voicebox-service: Manages job lifecycle, interacts with Spark Operator
- Spark Operator: Kubernetes operator for managing Spark applications
- voicebox-bites: Docker image containing the indexing application
- Spark Cluster: Dynamically created driver and executor pods
- Stardog: Database for indexed content and knowledge graphs
Prerequisites
Before deploying BITES, ensure:
- Kubernetes cluster (version 1.19+)
- kubectl configured to access your cluster
- Helm 3.x installed (for Spark Operator installation)
- Spark Operator installed in the cluster
- Access to voicebox-bites Docker image
- Stardog instance deployed and accessible from Kubernetes cluster
Step 1: Install Spark Operator
The Spark Operator manages the lifecycle of Spark applications in Kubernetes.
Installation via Helm:
# Add the Spark Operator Helm repository
helm repo add spark-operator https://kubeflow.github.io/spark-operator
# Update Helm repositories
helm repo update
# Install Spark Operator
helm install spark-operator spark-operator/spark-operator \
--namespace spark-operator \
--create-namespace \
--set webhook.enable=true \
--set sparkJobNamespace=default
Verify Installation:
kubectl get pods -n spark-operator
You should see the spark-operator pod running.
Alternative Installation Methods:
See the official Spark Operator documentation for other installation options.
Step 2: Configure Docker Image Access
The voicebox-bites image must be accessible from your Kubernetes cluster.
Option 1: Pull from Stardog JFrog Registry
Request access to the Stardog JFrog registry and configure an image pull secret:
kubectl create secret docker-registry stardog-jfrog-secret \
--docker-server=stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io \
--docker-username=YOUR_USERNAME \
--docker-password=YOUR_PASSWORD \
--docker-email=YOUR_EMAIL \
--namespace=default
Option 2: Push to Your Private Registry
- Pull the image from Stardog:
docker pull stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io/voicebox-bites:current - Tag and push to your registry:
docker tag stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io/voicebox-bites:current \ your-registry.com/voicebox-bites:current docker push your-registry.com/voicebox-bites:current - Update image reference in
vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
Step 3: Configure vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
The vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml file defines the Spark application specification.
Sample Configuration:
apiVersion: sparkoperator.k8s.io/v1beta2
kind: SparkApplication
metadata:
name: voicebox-bites-job
namespace: default
spec:
type: Python
pythonVersion: "3"
mode: cluster
image: "stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io/voicebox-bites:current"
imagePullPolicy: Always
imagePullSecrets:
- stardog-jfrog-secret
mainApplicationFile: local:///app/src/voicebox_bites/etl/bulk_document_extraction.py
sparkVersion: "3.5.0"
restartPolicy:
type: Never
driver:
cores: 2
coreLimit: "2000m"
memory: "4g"
labels:
version: 3.5.0
serviceAccount: spark-operator
executor:
cores: 2
instances: 3
memory: "4g"
labels:
version: 3.5.0
Key Configuration Sections:
Image Configuration:
image: "your-registry.com/voicebox-bites:current"
imagePullPolicy: Always
imagePullSecrets:
- your-image-pull-secret
Driver Configuration (controls the Spark driver):
driver:
cores: 2 # CPU cores for driver
coreLimit: "2000m" # Maximum CPU (Kubernetes format)
memory: "4g" # Memory allocation
serviceAccount: spark-operator
Executor Configuration (controls the Spark executors):
executor:
cores: 2 # CPU cores per executor
instances: 3 # Number of executor pods
memory: "4g" # Memory per executor
Sizing Guidelines:
| Dataset Size | Files | Executor Instances | Executor Memory | Executor Cores |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | <100 | 2-3 | 4g | 2 |
| Medium | 100-1000 | 4-6 | 8g | 4 |
| Large | 1000-10000 | 8-12 | 16g | 4 |
| Very Large | >10000 | 15-30 | 16g | 4 |
Important: BITES does not support Kubernetes autoscaling. Configure a fixed number of executor instances and do not scale down while jobs are running.
Step 4: Configure voicebox-service
The voicebox-service needs to know where to find the Spark configuration.
Set Environment Variable:
env:
- name: VBX_BITES_CONFIG_FILE
value: "/config/vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml"
Mount Configuration File:
volumes:
- name: bites-config
configMap:
name: vbx-bites-config
volumeMounts:
- name: bites-config
mountPath: /config
Create ConfigMap:
kubectl create configmap vbx-bites-config \
--from-file=vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml \
--namespace=default
Step 5: Configure RBAC
Ensure the voicebox-service has permissions to manage Spark applications.
Create Service Account:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: spark-operator
namespace: default
Create Role:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
name: spark-operator-role
namespace: default
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods", "services", "configmaps"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list", "delete", "update", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["sparkoperator.k8s.io"]
resources: ["sparkapplications"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list", "delete", "update", "watch"]
Create RoleBinding:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: spark-operator-rolebinding
namespace: default
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: spark-operator
namespace: default
roleRef:
kind: Role
name: spark-operator-role
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Apply RBAC Configuration:
kubectl apply -f spark-rbac.yaml
Step 6: Configure Networking
Ensure proper network connectivity between components.
Required Connectivity:
- Launchpad → voicebox-service (API calls)
- voicebox-service → Kubernetes API (Spark job management)
- Spark executors → Data sources (Google Drive, S3, etc.)
- Spark executors → Stardog (indexing)
- Spark executors → LLM providers (if using content enhancement or information extraction)
Firewall Rules:
- Allow outbound HTTPS (443) for data source APIs
- Allow outbound connections to Stardog endpoint
- Allow outbound connections to LLM provider APIs
Step 7: Deploy voicebox-service
Deploy the voicebox-service with the configured settings. The voicebox-service is a standard Kubernetes deployment that manages the lifecycle of BITES Spark jobs.
Requirements:
- Configuration: The
VBX_BITES_CONFIG_FILEenvironment variable must point to the Spark configuration file created in Step 4 - Spark Operator namespace: The Spark Operator must be configured to watch the namespace where voicebox-service creates SparkApplication resources. If voicebox-service creates jobs in a namespace other than where the Spark Operator was installed, ensure the operator’s
sparkJobNamespaceis set accordingly (see Step 1) - Network access: The service must be able to reach the Kubernetes API server to create and manage SparkApplication resources
- RBAC: The service account must have the permissions configured in Step 5 (create, get, list, delete SparkApplications and pods)
- Stardog connectivity: The service needs access to the Stardog endpoint for job status tracking
env:
- name: VBX_BITES_CONFIG_FILE
value: /config/vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
Ensure the voicebox-service pod mounts the same ConfigMap created in Step 4 so that VBX_BITES_CONFIG_FILE resolves correctly.
Cluster Sizing Recommendations
Minimum Cluster Size:
- 3 nodes
- 4 CPU cores per node
- 16 GB RAM per node
Recommended Production Cluster:
- 5-10 nodes
- 8 CPU cores per node
- 32 GB RAM per node
- 100 GB SSD per node (for temporary storage)
Scaling Considerations:
- Each executor needs dedicated resources
- Driver pod requires resources
- Kubernetes system pods consume resources
- Leave 20-30% capacity headroom
Do not enable cluster autoscaling for nodes running Spark executors. Scale the cluster before starting large jobs and maintain the size throughout job execution.
Logging
Comprehensive logging is essential for monitoring job execution and troubleshooting issues.
Logging Architecture
BITES provides two layers of logging:
- Spark Logging: Framework-level logs (job scheduling, task execution, etc.)
- BITES Application Logging: Application-level logs (document processing, API calls, etc.)
Spark Logging Configuration
Spark logging is configured using Log4j properties.
Setup Steps
- Create log4j.properties:
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, console
log4j.appender.console=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.console.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss} %p %c{1}: %m%n
# Reduce verbosity of some packages
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.storage=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.scheduler=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.util.Utils=WARN
log4j.logger.org.apache.spark.executor=INFO
Logging Levels:
ERROR: Only errorsWARN: Warnings and errorsINFO: Informational messages (recommended for production)DEBUG: Detailed debug information (use for troubleshooting only)TRACE: Very verbose (not recommended)
DEBUG and TRACE levels generate extremely large log volumes. Use only for troubleshooting specific issues.
- Create ConfigMap:
kubectl create configmap spark-log4j-config \
--from-file=log4j.properties \
--namespace=default
- Update vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml:
Add the following under spec:
spec:
sparkConf:
"spark.driver.extraJavaOptions": "-Dlog4j.configuration=file:/opt/spark/log4j.properties"
"spark.executor.extraJavaOptions": "-Dlog4j.configuration=file:/opt/spark/log4j.properties"
driver:
configMaps:
- name: spark-log4j-config
path: /opt/spark
executor:
configMaps:
- name: spark-log4j-config
path: /opt/spark
- Apply Configuration:
kubectl apply -f vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
BITES Application Logging
Application logging provides insights into document processing, API interactions, and business logic.
Setup Steps
- Create logging.conf:
[loggers]
keys=root,py4j
[logger_py4j]
level=WARN
handlers=nullHandler
qualname=py4j
propagate=0
[handlers]
keys=consoleHandler,nullHandler
[formatters]
keys=simpleFormatter
[logger_root]
level=INFO
handlers=consoleHandler
[handler_nullHandler]
class=logging.NullHandler
level=CRITICAL
args=()
[handler_consoleHandler]
class=voicebox_bites.logging_setup.FlushingStreamHandler
level=INFO
formatter=simpleFormatter
args=(sys.stdout,)
[formatter_simpleFormatter]
format=%(asctime)s %(levelname)s [%(job_id)s] %(name)s - %(message)s
Logging Levels:
INFO: Recommended for productionDEBUG: Detailed processing information (use for troubleshooting)
- Create ConfigMap:
kubectl create configmap voicebox-bites-log-config \
--from-file=logging.conf \
--namespace=default
- Update vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml:
Add the following to both driver and executor sections:
driver:
volumeMounts:
- name: vbx-bites-logging-config-volume
mountPath: /app/etc/logging.conf
subPath: logging.conf
executor:
volumeMounts:
- name: vbx-bites-logging-config-volume
mountPath: /app/etc/logging.conf
subPath: logging.conf
# Add under spec.volumes
volumes:
- name: vbx-bites-logging-config-volume
configMap:
name: voicebox-bites-log-config
- Apply Configuration:
kubectl apply -f vbx_bites_kube_config.yaml
Custom Log Path:
If you need to use a different path, set the VOICEBOX_BITES_LOG_CONF environment variable:
env:
- name: VOICEBOX_BITES_LOG_CONF
value: "/custom/path/logging.conf"
Accessing Logs
View Driver Logs
# Get driver pod name
DRIVER_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l spark-role=driver -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
# View logs
kubectl logs $DRIVER_POD
# Follow logs in real-time
kubectl logs -f $DRIVER_POD
# Save logs to file
kubectl logs $DRIVER_POD > driver.log
View Executor Logs
# List executor pods
kubectl get pods -l spark-role=executor
# View specific executor logs
kubectl logs voicebox-bites-job-exec-1
# View all executor logs
kubectl logs -l spark-role=executor
# Follow executor logs
kubectl logs -f voicebox-bites-job-exec-1
Centralized Logging
For production deployments with many executors, use centralized logging via a log aggregation stack such as ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), Fluentd, Grafana Loki, or your cloud provider’s native logging service.
BITES uses [vbx-bites][component] prefixes in all application log messages. Use the [vbx-bites] prefix to filter all BITES application logs:
*[vbx-bites]* AND level:ERROR
Troubleshooting
This section covers common issues and their solutions.
Permission Issues
Symptom
Error: Failed to create SparkApplication: User cannot create resource "sparkapplications"
Diagnosis
Check if the service account has the required permissions:
# Check permissions
kubectl auth can-i create sparkapplications --as=system:serviceaccount:default:spark-operator
# Check current role bindings
kubectl get rolebindings -o wide | grep spark-operator
Solution
Ensure proper RBAC configuration:
# Verify service account exists
kubectl get serviceaccount spark-operator
# Verify role exists and has correct permissions
kubectl describe role spark-operator-role
# Verify role binding
kubectl describe rolebinding spark-operator-rolebinding
# If missing, apply RBAC configuration
kubectl apply -f spark-rbac.yaml
See Step 5: Configure RBAC for complete RBAC configuration.
Data Source Authentication Errors
Google Drive: Authentication Failed
Symptom:
ERROR: Authentication failed: Invalid credentials
Common Causes:
- Service account JSON is not properly base64 encoded
- Service account doesn’t have access to the folder
- API not enabled in Google Cloud project
Solutions:
- Verify base64 encoding:
# Encode correctly cat service-account.json | base64 -w 0 # Test decoding echo "YOUR_BASE64_STRING" | base64 -d | jq . - Share folder with service account:
- Copy
client_emailfrom service account JSON - Share the Google Drive folder with this email
- Grant at least “Viewer” permissions
- Copy
- Enable Google Drive API:
- Go to Google Cloud Console
- Navigate to “APIs & Services” → “Library”
- Search for “Google Drive API”
- Click “Enable”
OneDrive/SharePoint: Invalid Client
Symptom:
ERROR: AADSTS7000215: Invalid client secret provided
Solutions:
- Regenerate client secret:
- Secrets expire after a configured period
- Go to Azure Portal → App registrations → Your app → Certificates & secrets
- Create a new secret
- Update credentials JSON and re-encode
- Verify permissions:
- Check that all required permissions are granted
- Ensure admin consent has been provided
- Wait 5-10 minutes after granting permissions
S3: Access Denied
Symptom:
ERROR: Access Denied (Service: Amazon S3; Status Code: 403)
Solutions:
- Verify IAM permissions:
{ "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3:ListBucket", "s3:GetObject" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket", "arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket/*" ] } - Check bucket policy:
- Ensure the bucket policy doesn’t deny access
- Verify the IAM role/user is allowed
- Verify region:
- Ensure
region_namein credentials matches bucket region
- Ensure
Job Execution Issues
Job Stuck in SUBMITTED State
Symptom: Job status remains “SUBMITTED” for extended period.
Diagnosis:
# Check Spark Operator logs
kubectl logs -n spark-operator -l app=spark-operator
# Check pending pods
kubectl get pods -l spark-role=driver
kubectl get pods -l spark-role=executor
# Describe pending pods
kubectl describe pod $DRIVER_POD_NAME
Common Causes:
- Insufficient cluster resources
- Image pull errors
- RBAC issues
Solutions:
- Insufficient resources:
# Check node resources kubectl describe nodes # Solution: Scale cluster or reduce resource requests - Image pull errors:
# Check events kubectl get events --sort-by='.lastTimestamp' # Solution: Verify image pull secret and image URL
Job Fails with Out of Memory (OOM) Error
Symptom:
ERROR: Executor lost: OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
Solutions:
- Increase executor memory:
executor: memory: "8g" # Increase from 4g - Reduce parallelism:
{ "content_reader_parallelism": 10 // Reduce from 30 } - Reduce batch size:
{ "batch_size": 500 // Reduce from 1000 } - Increase number of executors (distribute load):
executor: instances: 6 # Increase from 3 memory: "4g" # Keep same memory per executor
Job Fails with Rate Limit Errors
Symptom:
WARN: Rate limit exceeded for Google Drive API
Solutions:
- Reduce parallelism:
{ "list_file_parallelism": 3, "content_reader_parallelism": 5 }
2 Request quota increase from data source provider.
Indexing Issues
Documents Not Appearing in Voicebox
Diagnosis Steps:
- Verify job completed successfully:
curl -X GET "https://your-launchpad-url/api/v1/voicebox/bites/jobs/$JOB_ID" \ -H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_API_KEY" - Check driver logs for indexing confirmation:
kubectl logs $DRIVER_POD | grep "Indexed" - Verify Stardog contains data:
SELECT (COUNT(*) as ?count) WHERE { ?s ?p ?o }
Solutions:
- Job failed silently:
- Check logs for errors
- Rerun job with DEBUG logging
- Wrong database or graph:
- Verify Stardog connection details
- Check that Voicebox is querying the correct database/graph
- Stardog connectivity issue:
- Test connectivity from Spark executor to Stardog
- Check firewall rules
Logging Issues
No Logs Appearing
Diagnosis:
# Check if pods exist
kubectl get pods -l spark-role=driver
kubectl get pods -l spark-role=executor
# Check pod status
kubectl describe pod $POD_NAME
# Check if ConfigMaps mounted correctly
kubectl exec $DRIVER_POD -- ls -la /opt/spark
kubectl exec $DRIVER_POD -- ls -la /app/etc
Solutions:
- ConfigMap not mounted:
- Verify ConfigMap exists:
kubectl get configmap - Check volumeMounts in pod spec
- Verify path in VOICEBOX_BITES_LOG_CONF
- Verify ConfigMap exists:
- Wrong log level:
- Check logging configuration
- Ensure not set to ERROR or CRITICAL only
- Logs going to wrong destination:
- Verify log handler configuration
- Check stdout/stderr redirection
Logs Too Verbose
Solution:
Change log level from DEBUG to INFO:
For Spark Logs (log4j.properties):
log4j.rootCategory=INFO, console
For BITES Logs (logging.conf):
[logger_root]
level=INFO
Network Issues
Cannot Access Data Source
Symptom:
ERROR: Connection timeout when accessing data source
Solutions:
- Firewall blocking outbound connections:
- Allow HTTPS (443) egress
- Add data source domains to allow list
- Network policy blocking traffic:
- Review network policies
- Add exception for voicebox-bites pods
- DNS resolution issues:
- Check DNS configuration in cluster
- Verify CoreDNS is functioning
Cannot Connect to Stardog
Symptom:
ERROR: Connection refused: Stardog endpoint
Diagnosis:
# Test from driver pod
kubectl exec $DRIVER_POD -- curl -v http://stardog:5820/
# Check Stardog service
kubectl get svc stardog
Solutions:
- Stardog not accessible:
- Verify Stardog is running
- Check service endpoint
- Verify network policies
- Wrong endpoint:
- Check Stardog connection configuration
- Verify port (default 5820)
Getting Help
If you cannot resolve an issue:
- Collect diagnostic information:
- Job ID
- Driver and executor logs
- Spark Operator logs
- Job configuration
- Error messages
- Check documentation:
Docker Image Availability
Latest Version
Pull the most recent voicebox-bites image. The :current tag always points to the latest release:
docker pull stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io/voicebox-bites:current
Specific Versions
Pull a specific version. The current release is v0.3.0:
docker pull stardog-stardog-apps.jfrog.io/voicebox-bites:v0.3.0